The Integral Role of Barcodes in the Retail Industry
Barcodes are the foundation of modern retail operations, they transformed the industry with their remarkable efficiency. By converting data into machine-readable formats, they have reshaped retail landscapes. This technology enables retailers to effectively manage inventory, streamline sales processes, enhance customer experiences, and gain valuable business insights with accuracy and reliability.
In today's world, it's almost inconceivable to imagine a checkout process without barcodes. Furthermore, someone born in the 2000s likely can't envision how a store would operate without barcodes at the point of sale.
Inventory Management: Precision Beyond Basic Tracking
Inventory management undoubtedly stands as one of the most challenging and critical aspects of retail operations. Barcodes revolutionized this process, delivering unparalleled accuracy and real-time tracking of products throughout the entire supply chain. With every scan - whether a product arrives at the warehouse, moves to the sales floor, or is purchased at checkout - the inventory system instantly updates, ensuring absolute precision in stock management.
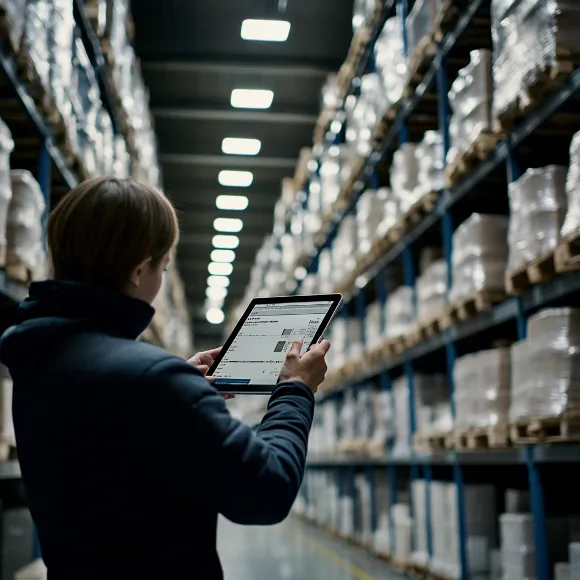

This real-time updating capability is the cornerstone of maintaining precise stock levels, effectively eliminating the risks of overstocking and stockouts. Overstocking no longer threatens to tie up valuable capital or inflate storage costs, while stockouts become a thing of the past, ensuring no missed sales opportunities or customer dissatisfaction. By leveraging a barcode-based system, retailers gain the power to accurately forecast demand, optimize inventory levels with precision, and make purchasing decisions backed by solid data.
Furthermore, barcodes have revolutionized the stocktaking process, transforming it from a tedious and error-prone manual task into a streamlined and highly accurate procedure. Traditional methods of counting inventory by hand were not only time-consuming but also susceptible to human error, leading to discrepancies that could have significant financial implications. With the introduction of barcode technology, staff members can now effortlessly scan items to verify stock levels, dramatically accelerating the entire process while simultaneously enhancing its precision.
As a direct result of these improvements, retailers can manage their inventory with unprecedented effectiveness. They can make more informed decisions about restocking, identify slow-moving items more quickly, and respond more rapidly to changes in demand. This level of inventory control not only optimizes operational efficiency but also enhances the overall customer experience by ensuring product availability and reducing instances of stockouts. In essence, the simplification of stocktaking through barcode technology has become a cornerstone of modern retail inventory management, enabling businesses to stay competitive in an increasingly dynamic market environment.
In retail inventory management, common barcode types include UPC (Universal Product Code) and EAN (European Article Number) for product identification at checkout, ITF-14 for tracking cases and pallets, and Code 128 for internal logistics and inventory control, offering a robust system for real-time tracking and accurate stock management. These barcodes streamline stocktaking, reduce errors, and enhance the overall efficiency of inventory processes.
Efficient Sales and Checkout Processes: Speed and Accuracy
The efficiency of the sales process directly affects customer satisfaction and a retailer's bottom line. Barcodes are crucial in speeding up the checkout process, enabling cashiers to scan products swiftly and accurately. This speed is especially vital during busy shopping periods, such as holidays or sales events, when long queues can result in lost sales and unhappy customers.
Beyond speed, barcodes help ensure pricing accuracy. Each barcode is linked to a product's price in the retailer’s database, meaning that when scanned, the correct price is automatically applied. This reduces the likelihood of pricing errors, which can occur when prices are entered manually. Accurate pricing not only prevents revenue loss but also builds trust with customers, as they are charged the correct amount every time.
 |  |  |
EAN/UPC code | Code 25 | Code 128 |
In addition to improving the speed and accuracy of transactions, barcodes also simplify the management of promotions and discounts. Retailers can easily update the pricing information in their systems for items on sale, and the changes are automatically reflected at checkout when the barcode is scanned. This capability ensures that promotional pricing is applied consistently and accurately across all transactions.
The ability to scan barcodes under various real-world conditions is crucial when selecting a scanning solution. BarKoder excels in this area with our deblur mode, specifically designed for EAN & UPC barcodes—the most common types used in retail. Additionally, our segment decoding algorithm effectively handles deformed or damaged 1D barcodes, further enhancing our scanning capabilities.
Customer Experience and Engagement: Personalization Through Technology
Barcodes are not just tools for operational efficiency; they are powerful drivers of enhanced customer experiences. In today's retail landscape, personalization reigns supreme.
Customers demand tailored offers and services that align perfectly with their preferences and shopping history. Barcodes are the key that unlocks this level of personalization, seamlessly connecting customer profiles with their purchase histories. This technology empowers retailers to deliver precisely what customers want, when they want it, creating a shopping experience that is both efficient and deeply satisfying.
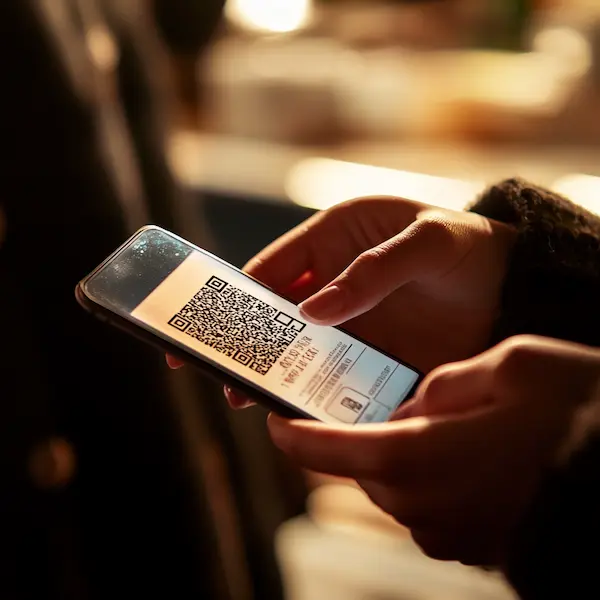

For instance, loyalty programs often rely on barcodes to track customer purchases. Each time a customer makes a purchase, the barcode on their loyalty card is scanned, and the transaction is recorded in their profile. Retailers can then use this data to offer personalized discounts, recommendations, or rewards, creating a more engaging and satisfying shopping experience.
Barcodes also play a role in self-service options, which are becoming increasingly popular in retail. Self-checkout systems, which allow customers to scan their items and complete transactions independently, rely heavily on barcode technology. These systems reduce wait times and provide customers with more control over their shopping experience, which can enhance satisfaction and encourage repeat business.
Additionally, barcodes can be used to provide customers with more information about products. Retailers can implement mobile apps that allow customers to scan a product’s barcode to access details such as ingredients, origin, or customer reviews. This transparency helps customers make informed purchasing decisions and builds trust in the brand.
Loyalty programs commonly use QR codes and Code 128 barcodes due to their ability to store customer data and be easily scanned. Other barcodes like EAN-13, PDF417, Data Matrix, and UPC are also used, depending on the program's needs and the type of information being tracked.
barKoder's SDK excels at reading QR and Data Matrix codes by utilizing our propriety algorithm called MatrixSight which is capable of scanning severely damages QR and Data Matrix codes.
Data-Driven Decision Making: Leveraging Barcodes for Business Insights
The data generated through barcode scanning is a valuable asset for retailers. Each scan captures information that can be analyzed to identify trends, optimize operations, and improve decision-making. Retailers can track sales patterns to determine which products are most popular, adjust inventory levels based on demand, and tailor marketing strategies to target specific customer segments.

Since the invention of the barcode, the market for handheld scanning applications has only grown. This figure was measured at $7.4 Billion in 2022, and is projected to grow to $13.3 billion by the year of 2032. Massive portion of this growth is as a result of the retail industries. For example, analyzing barcode data can help retailers identify peak shopping times, enabling them to adjust staffing levels accordingly to ensure optimal customer service. Similarly, sales data can reveal which products are frequently purchased together, informing cross-selling and upselling strategies that can increase average transaction values.
Barcodes also support better supply chain management. By tracking products from the manufacturer to the point of sale, retailers can monitor the performance of their supply chain, identify bottlenecks, and take corrective action to improve efficiency. This visibility is particularly important in today’s global retail environment, where supply chains are complex and subject to disruption.
In addition to operational insights, barcode data can inform broader business strategies. Retailers can use this data to forecast future trends, plan product launches, and evaluate the success of marketing campaigns. By integrating barcode data with other business intelligence tools, retailers can gain a comprehensive view of their operations and make data-driven decisions that drive growth and profitability.
How does this tie back to barKoder SDK?
The barKoder Barcode Scanning API transforms retail operations by turning smart devices into high-performing and cost-efficient barcode data capture tools. Our Barcode Scanner SDK combines fast, accurate, and flexible barcode scanning with an easy-to-integrate UI, making it the ideal solution for retail enterprises. It streamlines inventory management, speeds up checkout processes, and enhances customer experiences in retail environments.
barKoder Features
- Implement efficient inventory management systems with real-time tracking
- Streamline checkout processes, enhancing speed and accuracy
- Personalize customer experiences through data-driven insights
- Make informed business decisions based on comprehensive sales data
As mentioned before, customers can utilize our special features like:
to maximize their ability to use barcodes within their retail process.
If you want to improve your retail operations with barKoder SDK our documentation has everything you need to add our barcode scanning tech to your systems. For technical details and setup guides, check our documentation page.
Get started by requesting a quote. Our team will show you how barKoder can boost your inventory management, speed up checkouts, and provide key business insights using advanced barcode technology.




