Introduction to Barcodes in Healthcare
Barcodes have become essential in healthcare, improving patient safety, reducing errors, and boosting efficiency. These simple yet effective tools are now used throughout medical facilities, from hospitals to labs. Healthcare providers use barcodes to increase accuracy and efficiency in their daily work, leading to better patient care and smoother operations.
In today's fast-paced healthcare environment, where quick decisions can greatly impact lives, barcodes help maintain order and accuracy. They provide a common system for tracking, identifying, and managing important information across different healthcare processes.
We'll now look at how barcodes have changed medical practices. From making sure patients get the right medication to managing medical supplies accurately, barcodes have proven very useful. We'll explore the main ways barcode technology is shaping modern healthcare, improving patient care with each scan.
Medication Administration: Reducing Medication Errors
Barcodes play a critical role in ensuring patient safety and accuracy in medication administration. This technology serves as a vital safeguard against potential errors by enabling healthcare providers to verify the correct medication and dosage for each patient. The process involves a two-step verification: first, scanning the barcode on the medication packaging, and then scanning the patient's wristband.
This dual-scanning approach allows healthcare professionals to cross-reference the medication details with the patient's prescribed treatment plan, significantly reducing the risk of medication errors.
By implementing this barcode-based system, healthcare facilities can enhance their medication administration protocols, ultimately leading to improved patient outcomes and a higher standard of care. Furthermore, this technology not only ensures accuracy but also provides a digital trail for each medication administration, allowing for better tracking and accountability in healthcare settings.

Patient Identification
Barcodes are used for patient identification, linking them directly to their medical records and prescribed treatments. Patient wristbands with barcodes are scanned to confirm the correct medication and treatment plan, reducing the risk of errors.

Medical Inventory Management: Enhancing Surgical Safety
Barcodes help track medical supplies and equipment, allowing healthcare providers to monitor inventory levels efficiently. This tracking capability ensures timely restocking of essential items, preventing shortages and optimizing resource use.
In surgical settings, barcodes are used to track surgical instruments and ensure they are properly sterilized before use. Barcoded trays and instruments help prevent the accidental retention of surgical tools inside patients, a rare but serious medical error. Additionally, barcodes can track the usage of implants and other surgical materials, ensuring that patients receive the correct implants and that these are properly documented.
_1100328000.webp)
Laboratory Testing
In laboratory settings, during laboratory testing, barcodes play a role in specimen tracking and management. This ensures precise labeling and accurate patient matching, significantly reducing the risk of errors in sample handling.
By implementing barcode systems, laboratories can maintain a high level of integrity throughout the testing process, from specimen collection to result reporting.
The use of barcodes creates a robust chain of custody for each sample, allowing for seamless tracking and identification at every stage of analysis. Furthermore, this system enhances the overall efficiency of laboratory operations by streamlining workflows and minimizing manual data entry. Perhaps most importantly, barcode technology provides a reliable method for connecting test results to the correct patient records, thereby enhancing patient safety and improving the quality of healthcare delivery.

Blood Transfusion Management : Preventing Errors
Barcodes play a critical role in blood transfusion management, serving as a vital safeguard to ensure patients receive the correct blood type. This technology significantly enhances patient safety by providing a robust system for verifying blood compatibility. The process involves a meticulous two-step verification: healthcare providers scan both the barcode on the blood bag and the patient's wristband before administering any transfusion. This dual-scanning approach allows for a thorough cross-reference between the blood product and the patient's specific blood type and transfusion requirements.

By implementing this barcode-based system, healthcare facilities can dramatically reduce the risk of potentially life-threatening blood type mismatches. The technology not only ensures accuracy but also provides a digital trail for each transfusion, allowing for better tracking and accountability. This level of precision and documentation is particularly crucial in emergency situations where rapid, error-free transfusions can be life-saving. Furthermore, the use of barcodes in blood transfusion management contributes to overall efficiency in healthcare settings, streamlining the process while maintaining the highest standards of patient care and safety.
Innovations in Barcode Technology in Healthcare
RFID and Barcodes
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology is increasingly used alongside traditional barcodes to enhance tracking and identification in healthcare. RFID tags can store more data and do not require line-of-sight scanning, making them ideal for tracking high-value medical equipment, patient movements, and even medications. Combined with barcode systems, RFID can improve efficiency and accuracy in various healthcare processes.

Smart Barcodes
Smart barcodes, like QR codes and Data Matrix codes, can store more complex information than traditional linear barcodes. These two-dimensional barcodes are being used to store comprehensive patient information, such as allergies, medical history, and treatment plans. Smart barcodes can also link to online databases or electronic health records (EHRs), allowing healthcare providers to access detailed patient information instantly.
 |  |
Wearable Barcode Technology
Wearable barcode technology, such as wristbands with embedded barcodes, has become standard in many hospitals. These wristbands not only provide a means of patient identification but can also track patient movements within a healthcare facility, monitor vital signs, and integrate with hospital information systems to provide real-time data updates.

Types of Barcodes Used in Healthcare
Code 128
Code 128 is a high-density linear barcode that encodes alphanumeric characters. It is widely used in healthcare for medication labeling, patient identification, and inventory management.

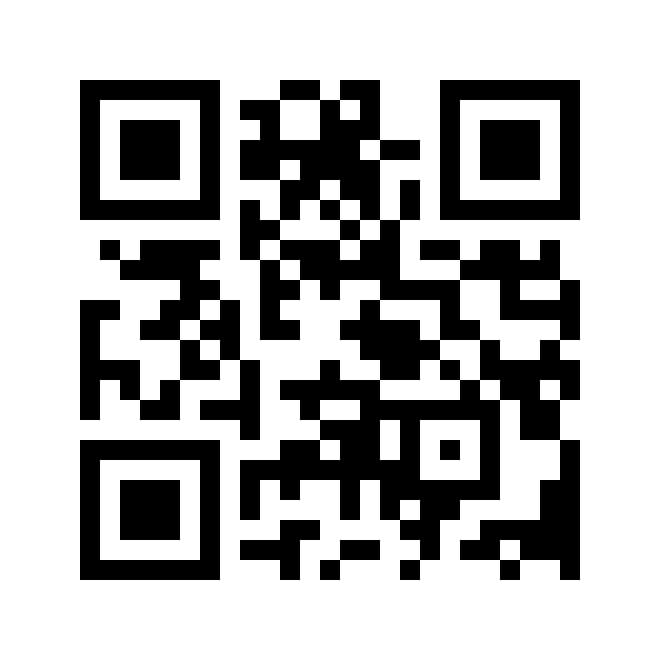
QR Code
QR Codes are two-dimensional barcodes capable of storing large amounts of data, including text and images. They are used for patient identification, medical record keeping, and tracking medical equipment.

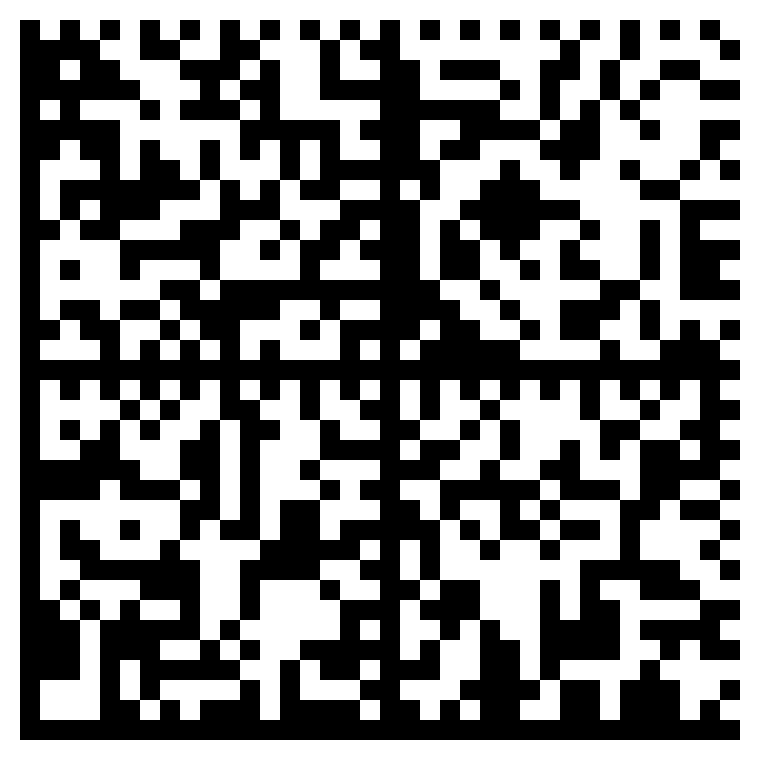
Data Matrix
Data Matrix barcodes are similar to QR codes but are more compact. They are commonly used in healthcare for tracking medical products and supplies due to their ability to store significant amounts of data.

Code 39
Code 39 is a linear barcode that encodes both letters and numbers. It is often utilized in healthcare for medication labeling, patient identification, and managing inventory.

PDF417
PDF417 is a two-dimensional barcode that can store vast amounts of data, including text and images. It is used for patient identification, medical record keeping, and equipment tracking.

Interleaved 2 of 5
Interleaved 2 of 5 is a linear barcode that encodes numeric data. It is frequently used for inventory management and tracking medical products.

Code 93
Code 93 is used in healthcare for inventory management, tracking medical supplies, and patient identification.

Aztec Code
Aztec Codes are useful for patient identification and medical records management. Their compact size allows for storing detailed medical information, making them ideal for healthcare applications.

That's all nice but how can the barKoder SDK help you?
The barKoder SDK boosts healthcare operations with fast, accurate barcode scanning. It easily fits into existing systems, works across platforms, and uses top-notch scanning tech. This tool makes patient care safer, keeps track of supplies better, and helps healthcare places run smoother overall.
barKoder Features
- Patient Safety: The SDK can enhance patient safety by enabling accurate barcode scanning for medication administration and patient identification.
- Inventory Management: It can improve tracking of medical supplies, helping healthcare facilities manage their inventory more efficiently.
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: The SDK works across different platforms, making it versatile for various healthcare settings.
- Integration: It can be easily integrated into existing healthcare systems, streamlining the implementation process.
- Overall Efficiency: By utilizing advanced scanning technology, the barKoder SDK can contribute to smoother operations in healthcare facilities.
As mentioned before, customers can utilize our special features like:
to maximize their ability to use barcodes within their healthcare solutions.
If you want to improve your operations with barKoder SDK, our documentation has everything you need to add our barcode scanning tech to your systems. For technical details and setup guides, check our documentation page.
Get started by requesting a quote. Our team will show you how barKoder can boost your inventory management, speed up checkouts, and provide key business insights using advanced barcode technology.