
How postal barcodes work and what they mean
What is a Postal Code?
A postal code is a series of letters, numbers, or both, assigned to specific geographic areas to facilitate mail sorting and delivery. Used by postal services worldwide, postal codes ensure that mail and packages reach their intended destinations efficiently. These codes play a crucial role in logistics, transportation, and even demographic analysis.
History of Postal Codes
The concept of postal codes originated in the early 20th century as a means to improve mail distribution. The first known postal code system was introduced in Ukraine (then part of the Soviet Union) in 1932. Other countries soon followed, with the United States implementing ZIP codes in 1963 and the United Kingdom introducing postcodes in the 1950s. Today, most countries have their own standardized postal code systems.

Structure of Postal Codes
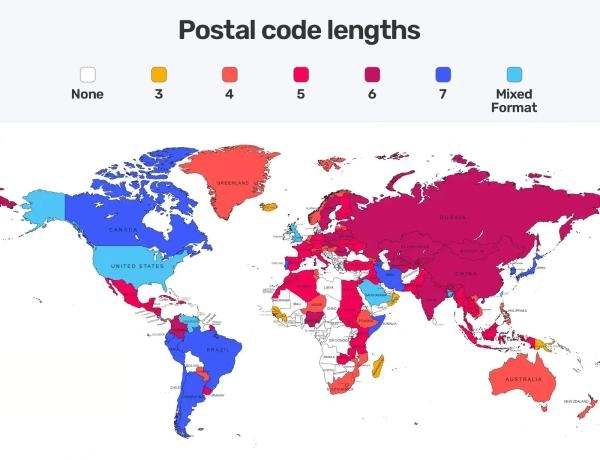
Postal codes vary in format from country to country. Here are a few examples:
- United States: Uses a five-digit ZIP code, sometimes followed by a four-digit extension (e.g., 10001-2345).
- United Kingdom: Uses alphanumeric postcodes with a mix of letters and numbers (e.g., SW1A 1AA).
- Canada: Uses a six-character alphanumeric format (e.g., M5V 3L9).
- Germany: Uses a five-digit numeric code (e.g., 10115).
- India: Uses a six-digit numeric PIN code (e.g., 110001).

Japan Post barcode
The Japan Post barcode, specifically known as the Japan Post 4-State Customer Code, is a specialized barcode system used primarily by Japan Post for efficient mail processing and tracking.This barcode system plays a crucial role in automating sorting, delivery, and tracking of mail items within Japan, utilizing a compact and highly efficient coding scheme. Below is a detailed exploration of the Japan Post barcode technology, its structure, encoding principles, applications, advantages, and usage scenarios.

Structure of the Japan Post Barcode
The Japan Post Barcode consists of several key components:
Start Character: A unique pattern that signifies the beginning of the barcode.
Encoded Postal Code: The main body of the barcode, representing the numerical postal code in binary form.
Check Digit: A single digit used for error detection.
Stop Character: A unique pattern that signifies the end of the barcode.
Here are some common barcode types used by Japan Post:
Tracking Number Barcode (for parcels and EMS)
- Japan Post uses Code 128 barcodes for tracking numbers.
- A typical Japan Post tracking number is 13 characters long, e.g., EE123456789JP.
- The barcode represents this number for scanning at sorting facilities.
Postal Code Barcode (カスタマバーコード / Customer Barcode)
- Japan Post assigns a customer barcode (カスタマバーコード) based on postal codes.
- It is a customized numeric barcode used to speed up mail sorting.
- Usually seen on letters and postcards.
Yu-Pack / Yu-Mail Barcodes
- Uses a QR code or Code 39/128 barcode on shipping labels.
- This barcode is linked to Japan Post’s tracking system.
JP Bank (ゆうちょ銀行) Payment Barcodes
- QR codes are commonly used for online payments or money transfers.
PLANET barcode & Error correction of the PLANET barcode
The PLANET barcode (Postal Alpha Numeric Encoding Technique) is a linear barcode symbology developed by the United States Postal Service (USPS) to track mail pieces during delivery. While PLANET barcodes themselves do not inherently include robust error correction mechanisms like some modern barcode symbologies (e.g., QR codes with Reed-Solomon error correction), certain principles and methods are used to ensure their accuracy and reliability in practical applications. This document provides a detailed exploration of error correction techniques as they pertain to PLANET barcodes.

1. Error Detection Methods
1.1 Checksum Calculation
PLANET barcodes utilize a checksum digit to help detect errors in the encoded data. The checksum is calculated by summing the values of the digits in the barcode and then performing a modulus operation.
Example: For a PLANET code '12345678901', the checksum is calculated as follows:
Sum of digits: 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 + 6 + 7 + 8 + 9 + 0 + 1 = 46
Modulus operation (mod 10): 46 % 10 = 6
The checksum digit is 6, so the final encoded barcode is '123456789016'.
1.2 Parity Checks
Parity checks can be used to detect single-bit errors by ensuring that the number of bits with the value '1' is even (even parity) or odd (odd parity).
Example: For a simplified PLANET code '11010101', an even parity bit would be appended to make the total number of '1's even. If the count of '1's is already even, the parity bit is '0'; if odd, the parity bit is '1'.
1.3 Redundant Encoding
Some implementations might use redundant encoding, where critical parts of the data are repeated within the barcode. This helps in verifying the integrity of the data if part of the barcode is damaged or misread.
Uses of Postal Codes
Apart from mail delivery, postal codes are used for various other purposes, including:
- Navigation & Address Verification: Many online services use postal codes for geolocation and address validation.
- E-commerce & Logistics: Shipping companies use postal codes to determine delivery routes and estimate shipping costs.
- Emergency Services: Postal codes help emergency responders quickly locate addresses.
- Demographics & Marketing: Businesses use postal code data to analyze customer demographics and plan marketing campaigns.
Conclusion
Postal codes are an essential part of modern infrastructure, simplifying mail delivery and enabling efficient logistics. Whether you’re sending a letter or ordering something online, postal codes ensure that addresses are easily identifiable, making everyday transactions smoother and more reliable. Understanding postal codes can help you navigate and utilize various services more effectively.
The new SDK version is readily available and can be obtained by simply registering on the barKoder Portal. Each registered account has the opportunity to generate a completely free trial license for an initial period of 30 days. This trial offers you a full chance to evaluate the capabilities of our mobile and web barcode scanner SDK for up to 25 devices. If your project has different requirements, we are more than willing to hear from you or just utilize the Ticketing System of the barKoder Developer Portal and find solutions that meet your needs.






